Over the last decade, biologic therapeutic proteins have advanced the treatment of many diseases with therapeutic antibodies such as infliximab, adalimumab, rituximab, tocilizumab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, just to mention a few. One limitation for the use of therapeutic antibodies is immunogenicity, the induction of antibodies by the adaptive immune system in response to foreign substances.
There are many factors that influence the immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals, and although in most cases an immune response to a biopharmaceutical has little or no clinical impact, they do pose several potential risks for the patient.


Over the last decade, biologic therapeutic proteins have advanced the treatment of many diseases with therapeutic antibodies such as infliximab, adalimumab, rituximab, tocilizumab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, just to mention a few. One limitation for the use of therapeutic antibodies is immunogenicity, the induction of antibodies by the adaptive immune system in response to foreign substances.
There are many factors that influence the immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals, and although in most cases an immune response to a biopharmaceutical has little or no clinical impact, they do pose several potential risks for the patient.
This immunogenetic response, where antibodies are produced by the immune system as a protective reaction, can adversely affect the pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and efficacy of the drug, and may neutralize the activity of the drug. Assessment of drug immunogenicity (IMG) is a regulatory requirement and is considered part of the safety evaluation that all biopharmaceutical drugs undergo.
Hence, the development of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) following the administration of biotherapeutics to patients is a vexing problem that is attracting increasing attention from pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. The clinically most relevant fraction of these antibodies is the neutralizing anti-drug antibodies (NAbs) that block the pharmacological function of the drug.
Consequently, the detection of NAbs in plasma is a better predictor of loss of therapeutic response than increased levels of total anti-drug antibodies (ADA). Traditional assays to detect ADA and NAb have limited specificity, sensitivity, and linear dynamic range.
The purpose of assessing and determining this is to provide drug developers (and clinicians once the drug is released on the market) with information regarding the effect of neutralizing antibodies on the sustainable efficacy of therapies. This information will be of value to predict and assess risk, during the earlier development stages and also clinical outcome in the later stages as well as key information for practitioners who should take into account the potential for changes in the efficacy and safety of biologic therapies and closely monitor patients under their care.
The standard approach , when determined the immunogenicity profile of a drug compound, is to measure ADAs and NAbs in a multi-tiered approach.
1. During the first tier a screening assay is used, where the focus is on detecting ADAs that bind to the biological drug. This is usually carried out in ligand binding ELISA assays to detect ALL types of binding.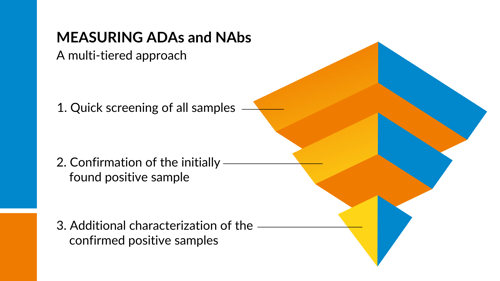
By combing LBA (ligand binding assay) immunogenicity knowledge with a cell-based assay, a full characterization of ADAs and NAbs in the tiered approach can be achieved.
This means more information and a better understanding of the immune system compounds to develop your risk mitigation strategy - the more informed choices you can make, the more likelihood of your projects having a successful outcome.
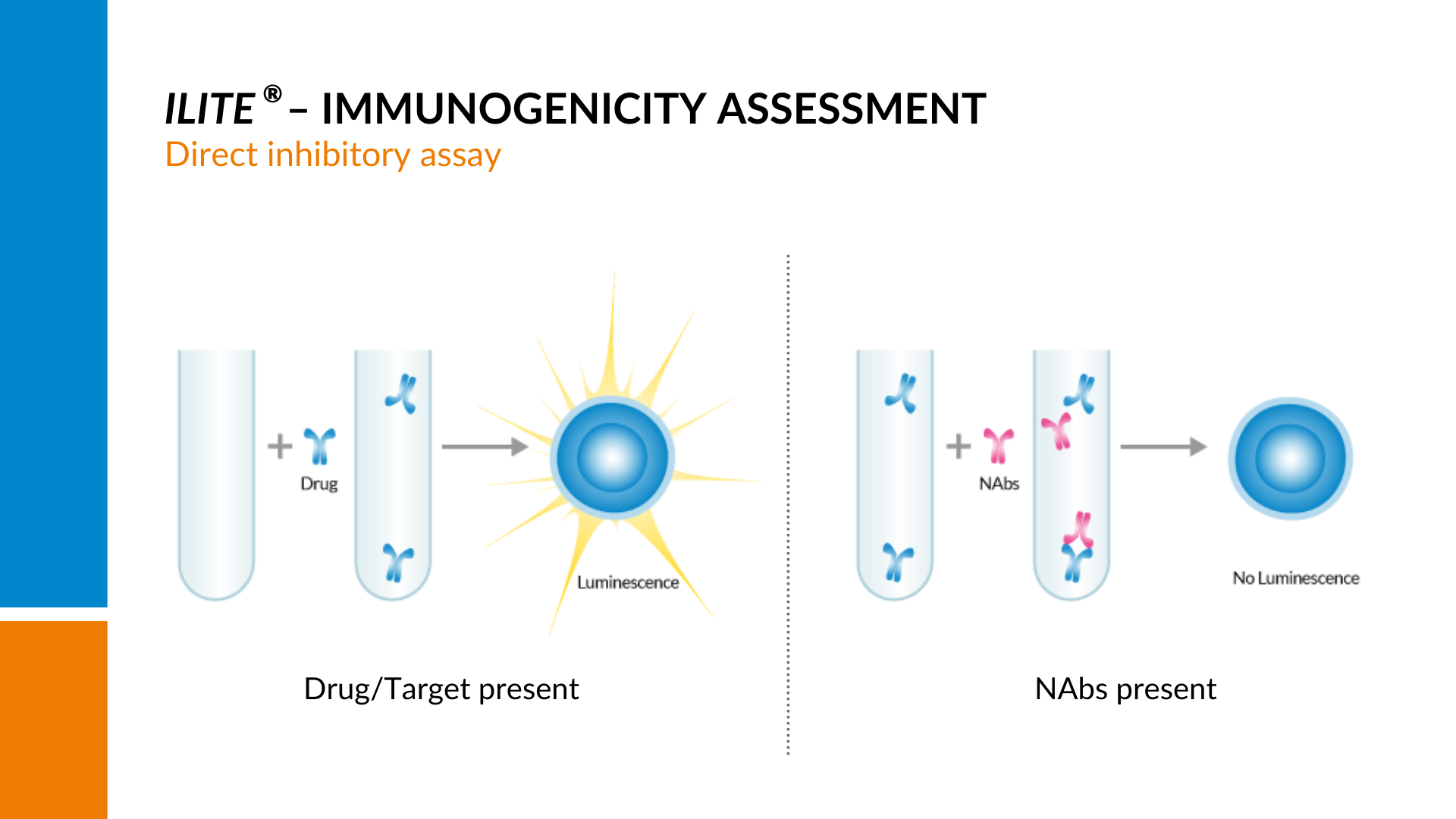
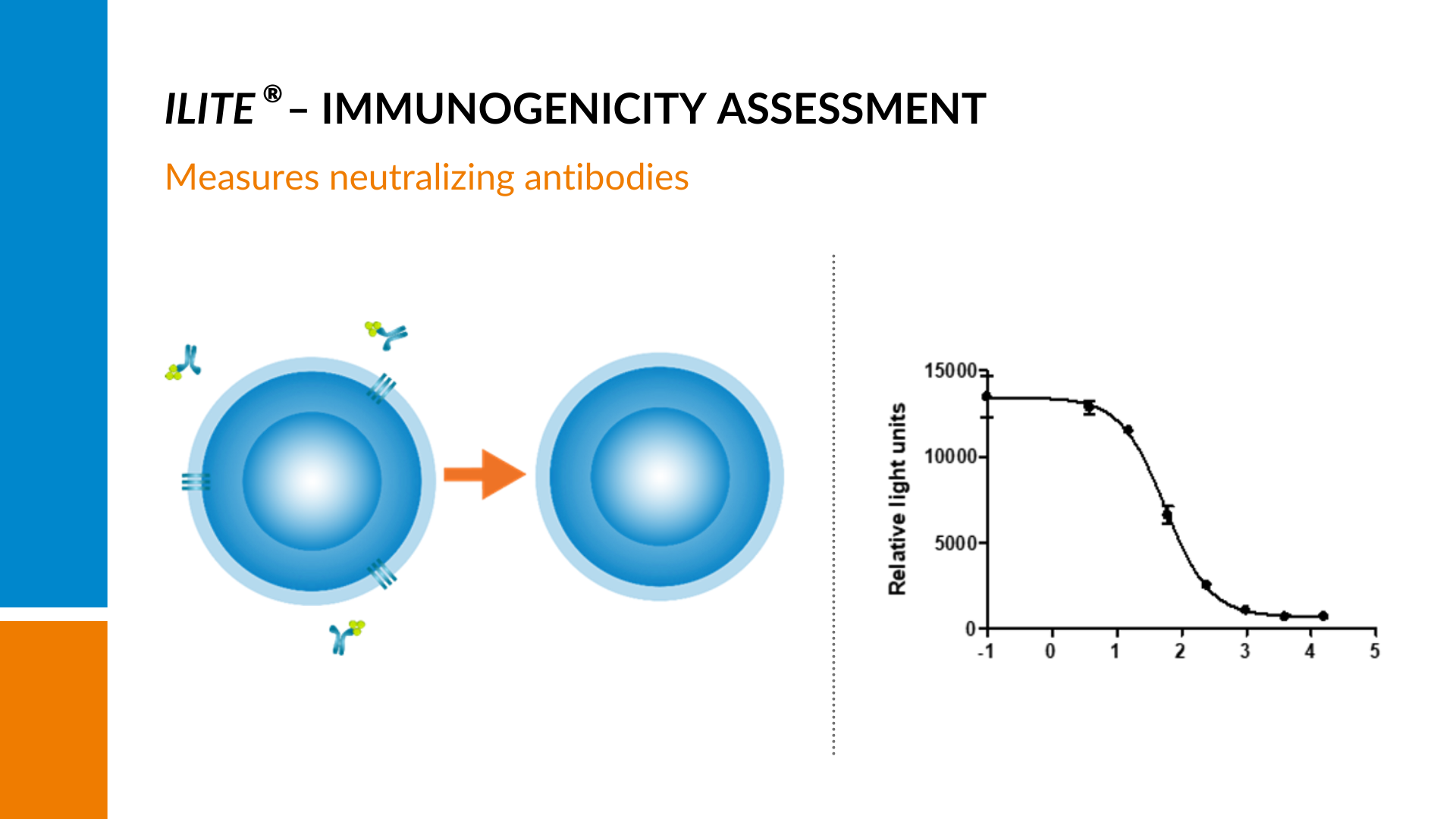
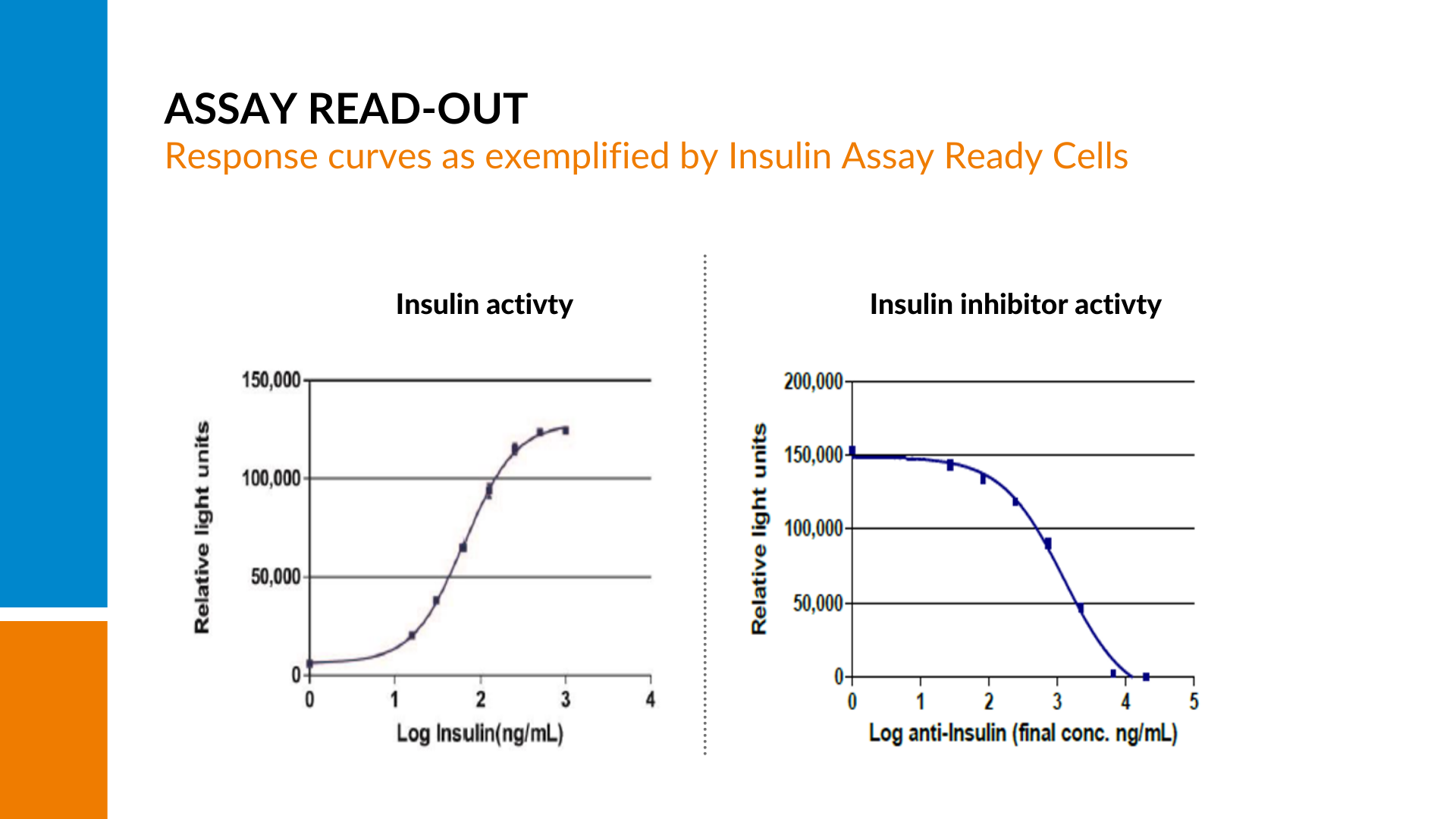
A set dose-dependent signal is generated by stimulating the cells with their target.
If there are neutralizing antibodies present in the sample, the amount of free drug to stimulate the cells will be reduced, resulting in a quenching of the signal and a decline in the curve with increasing amounts of neutralizing antibodies present.