DIAGNOSTIC TEST PANEL 555
Inflammatory Myopathies (Myositis)/Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Diagnostic test panel for antibodies against cN-1A, HMGCR, Mi-2α, Mi-2β, TIF1γ, MDA5, NXP2, SAE1, Ku, PM-Scl100, PM-Scl75, Jo-1, SRP, PL-7, PL-12, EJ, OJ, and Ro-52. For suspicion of inflammatory myopathies, myositis (polymyositis - PM, dermatomyositis - DM, overlap syndrome, inclusion body myositis – IBM, or immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy - IMNM).
Indication
Suspicion of inflammatory myopathies, myositis (polymyositis - PM, dermatomyositis - DM, overlap syndrome, inclusion body myositis - IBM or immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy - IMNM).
Clinical background
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (myositis) constitute a heterogeneous group of diseases of which many have a presumed autoimmune origin. Dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), and inclusion-body myositis (IBM) are the main representatives of this group including the anti-synthetase syndrom. Myositis can also be seen in association with rheumatic disorders. Myositis is most often characterized by muscle weakness but involvement of joints, skin and lungs may also occur and even dominate the clinical picture. An elevation of creatine kinase in blood is a typical laboratory finding but can be discrete.
The diseases are in some cases considered immune mediated by infiltration of T-cells in the affected tissue while others are dominated by humoral immunity and/or activation of macrophages. In recent years, several autoantibodies have been identified as useful markers for subtypes of myositis. This is of great importance for diagnosing as well as prognosing and choosing optimal therapy. Myositis can be associated with underlying cancer (i. e. paraneoplastic origin) and occur years before the tumor is diagnostically detectable. Myositis-specific autoantibodies are directed against cytoplasmic or nuclear components involved in key regulatory intracellular processes such as protein synthesis and gene transcription.
Myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSAs): Jo-1 (Histidyl-tRNA-Synthetase), PL-7 (Threonyl-tRNA-Synthetase), PL-12 (Alanyl-tRNA-Synthetase), EJ (Glycyl-tRNA-Synthetase), OJ (Isoleucyl-tRNA-Synthetase), Mi-2, SRP (Signal Recognition Particle), KS (Asparaginyl-tRNA-Synthetase), TIF1γ/α, TIF1β, MJ/NXP2, MDA5/CADM140, SAE (SUMO-1)
Myositis-associated autoantibodies (MAAs): PM-Scl75, PM-Scl100, Ku, U1RNP, U1/U2RNP, U3RNP
Other autoantibodies often found in myositis: Ro52, Ro60, Su/Ago2.
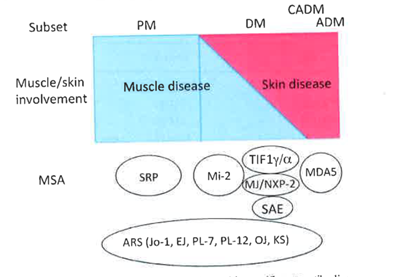
Fig.1 Overview of the association of MSAs with the spectrum of muscle and skin involvements in different subsets of PM/DM. It varies from muscle disease without skin disease (PM), involvement of both muscle and skin with different degrees of each (DM), to skin disease with minimal muscle involvement (CADM) or no muscle involvement (ADM). Anti-ARS (aminoacyl tRNA synthetase) is detected in both PM and DM and occasionally in ADM. Figure from Satoh M. et al. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol (2017) 52:1-19. PMID: 26424665.
References
- Satoh M. et al. A Comprehensive Overview on Myositis-Specific Antibodies: New and Old Biomarkers in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy, Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol (2017) 52:1-19. PMID: 26424665
- Fujimoto M et al. Recent advances in dermatomyositis-specific autoantibodies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016 Nov;28(6):636-44. PMID: 27533321
- Nakashima R Et al. Clinical significance and new detection system of autoantibodies in myositis with interstitial lung disease, Lupus (2016) 25, 925-933. PMID: 27252271
- Trallero Arguas E et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. Clinical manifestations and long-term outcome of anti-Jo1 antisynthetase patients in a large cohort of Spanish patients from the GEAS-IIM group. 2016 Oct;46(2):225-31. PMID: 27139168
- Allenbach Y, Benveniste O. Diagnostic Utility of Auto-Antibodies in Inflammatory Muscle Diseases, Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases 2 (2015) 13-25. PMID: 28198709
- Ghirardello A. et al. Myositis autoantibodies and clinical phenotypes, Autoimmun Highlights (2014) 5:69-7. PMID: 26000158
- Beneviste et al, Arthritis Rheum 2011;63(7):1961. Correlation of anti-signal recognition particle autoantibody levels with creatine kinase activity in patients with necrotizing myopathy. PMID: 21400483 (SRP artikel)
- Belizna C. et al. Anti-Ku antibodies: Clinical, genetic and diagnostic insights. Autoimmunity Reviews 2010;9:691. PMID: 20621654 (bra översiktsartikel om anti-Ku)
- Gunawardena H, Betteridge ZE, McHugh NJ. Myositis-specific autoantibodies: their clinical and pathogenic significance in disease expression, Rheumatology 2009;48:607-612. PMID: 19439503
-
Mahler M et al. Novel aspects of autoantibodies to the PM/Scl complex: clinical, genetic and diagnostic insights. Autoimmunity Reviews 2007;6:432. PMID: 17643929 (bra översiktsartikel om anti-PM-Scl)
Tests included in panel
Need pricing information?
How to order
This test panel is available worldwide for hospitals, clinics, and physicians.
-
Print and complete the request form
Download the request form. Clearly state the name and phone number of the referring hospital, clinic, or physician. -
Prepare your samples
Serum: At least 1 mL serum (plain serum tubes without additives).
-
Send samples and request form
Within Sweden
Samples can be sent at room temperature to:
Envelopes and smaller boxes:
Wieslab AB, Box 50117, 20211 Malmö, Sweden
Larger boxes and frozen samples:
Wieslab AB, Lundavägen 151, 21224 Malmö, Sweden
International
Samples can be sent at room temperature to:
Wieslab AB, Lundavägen 151, 21224 Malmö, Sweden
Last updated: 2025-08-18
