- Other Products
- CCP
Svar Life Science has a long and proud history of offering products and services for the study of the complement system. Our assays were developed in collaboration with key opinion leaders in the complement system field to offer fast and reliable results, whether you use our functional assays or our individual biomarker assays.

Svar Life Science has a long and proud history of offering products and services for the study of the complement system. Our assays were developed in collaboration with key opinion leaders in the complement system field to offer fast and reliable results, whether you use our functional assays or our individual biomarker assays.
We are now happy to announce the addition of a cell-based C5a assay to our complement system portfolio. With this product, we have combined our expertise in complement system biology with our long experience and knowhow in cell-based assays, to create a new iLite cell-based functional assay. This assay is ideal for potency measurements of anti-C5a candidate drugs. It can be used to study C5a, receptor C5aR1 and their interactions in test samples, including human serum. In addition, it can be used to measure the effects of other small-molecule C5a antagonists.
Our C5a reporter-gene assay comes in an assay-ready format, which translates to a fast, streamlined work process with low variability.
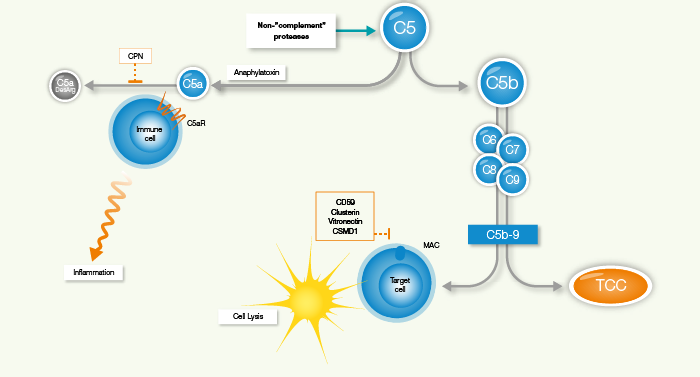
The complement system is a key component of the innate immune system and plays an important role in defending the body against infection. However, deficiencies or overactivation can instead cause harm to the body, which has made the complement system a promising target for therapeutics. Since the complement system consists of over 30 proteins there are many potential targets to choose from.
The first drug to be approved was eculizumab, which is an antibody against complement component C5. This drug is used to treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) and works by preventing C5 from being cleaved into C5a and C5b. There is great interest in developing additional C5 inhibitors, as this protein appears to play a role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). C5a is of special interest as it accumulates in the joints and blood of RA patients. In contrast to C5, C5a does not contribute to the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), which could potentially mean that C5a inhibitors are less likely to cause oversensitivity to infections.
The development of new anti-C5a and anti-C5a receptor drugs require a good model that closely resembles the environment of the body. Our new C5a iLite assay offers a fast and accurate cell-based assay, ideal for use in the development of such therapeutics.
Go to the product page